About Kubesphere
KubeSphere is a member of CNCF and a Kubernetes Conformance Certified platform, further enriching CNCF CLOUD NATIVE Landscape.
 KubeSphere is a distributed operating system for cloud-native application management, using Kubernetes as its kernel. It provides a plug-and-play architecture, allowing third-party applications to be seamlessly integrated into its ecosystem.
KubeSphere is a distributed operating system for cloud-native application management, using Kubernetes as its kernel. It provides a plug-and-play architecture, allowing third-party applications to be seamlessly integrated into its ecosystem.
KubeSphere also represents a multi-tenant enterprise-grade Kubernetes container platform with full-stack automated IT operation and streamlined DevOps workflows.
It provides developer-friendly wizard web UI, helping enterprises to build out a robust and feature-rich platform.
Need for Kubesphere
It boasts the most common functionalities needed for enterprise Kubernetes strategies, such as Kubernetes resource management, DevOps (CI/CD), application lifecycle management, monitoring, logging, service mesh, multi-tenancy, alerting and notification, auditing, storage and networking, autoscaling, access control, GPU support, multi-cluster deployment and management, network policy, registry management, and security management.
Features of Kubesphere
Kubernetes provide you with:
O&M Friendly
KubeSphere hides the details of underlying infrastructure for users and helps enterprises modernize, migrate, deploy and manage existing and containerized apps seamlessly across a variety of infrastructure types.
This is how KubeSphere empowers developers and Ops teams to focus on application development and accelerate DevOps automated workflows and delivery processes with enterprise-level observability and troubleshooting, unified monitoring and logging, centralized storage and networking management, easy-to-use CI/CD pipelines, and so on.
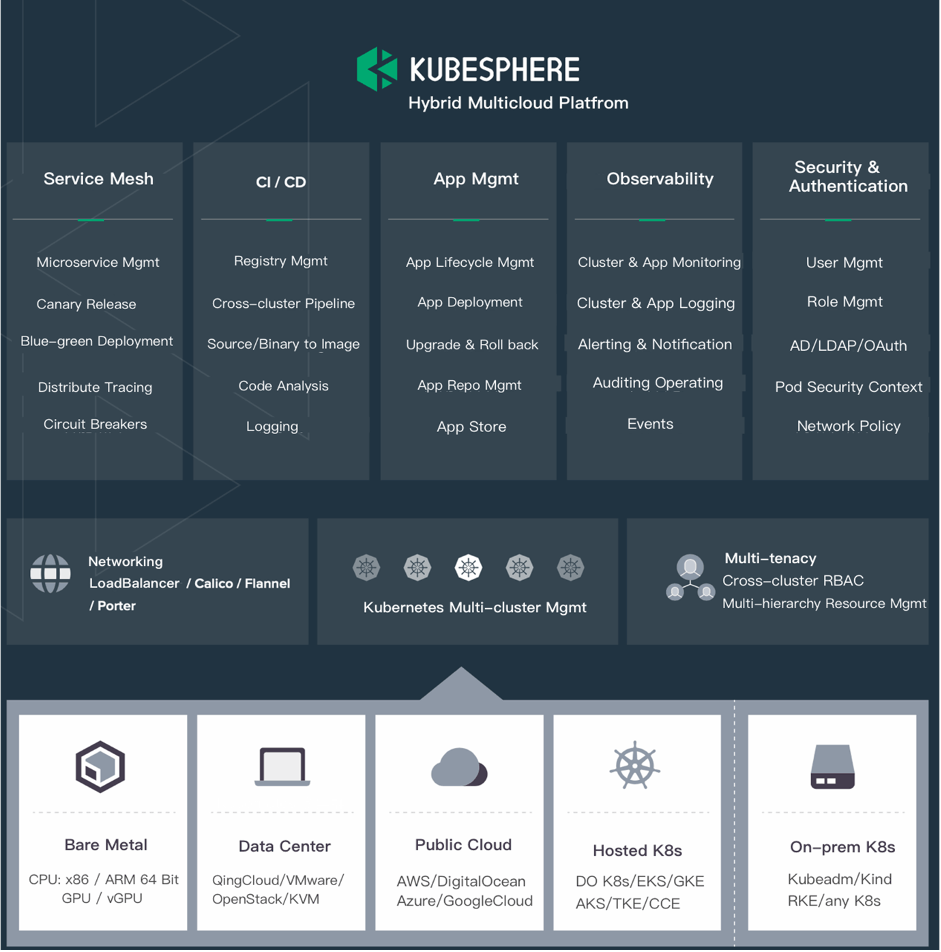
Run KubeSphere Everywhere
As a lightweight platform, KubeSphere has become more friendly to different cloud ecosystems as it does not change Kubernetes itself at all. In other words, KubeSphere can be deployed on any existing version-compatible Kubernetes cluster on any infrastructure including virtual machine, bare metal, on-premises, public cloud and hybrid cloud.
Open Source
With the open-source model, the KubeSphere community advances development in an open way. KubeSphere is 100% open source and available on GitHub where you can find all the source code, documents and discussions. It has been widely installed and used in development, testing and production environments, and a large number of services are running smoothly in KubeSphere.
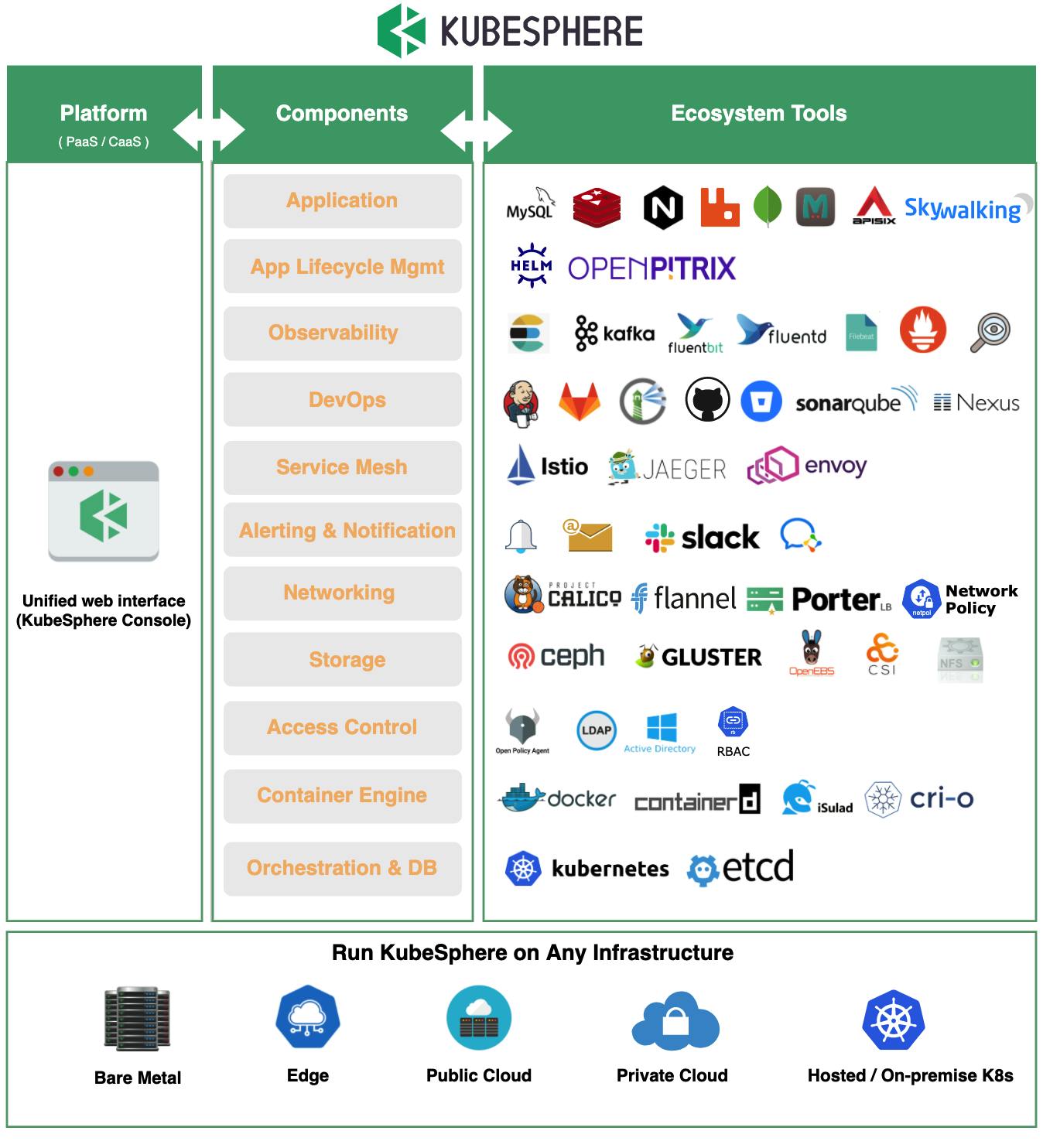
KubeSphere Ecosystem Tools
Abundant Ecosystem Tools
KubeSphere integrates a wide breadth of major ecosystem tools related to Kubernetes, ranging from cloud-native apps to the underlying container runtimes. These open-source projects serve as the backend components of KubeSphere, which interact with the KubeSphere console through standard APIs, thus providing consistent user experiences to reduce complexity.
KubeSphere also features new capabilities that are not yet available in upstream Kubernetes, alleviating the pain points of Kubernetes including storage, network, security and usability. Not only does KubeSphere allow developers and DevOps teams use their favorite tools in a unified console, but, most importantly, these functionalities are loosely coupled with the platform since they are pluggable and optional.
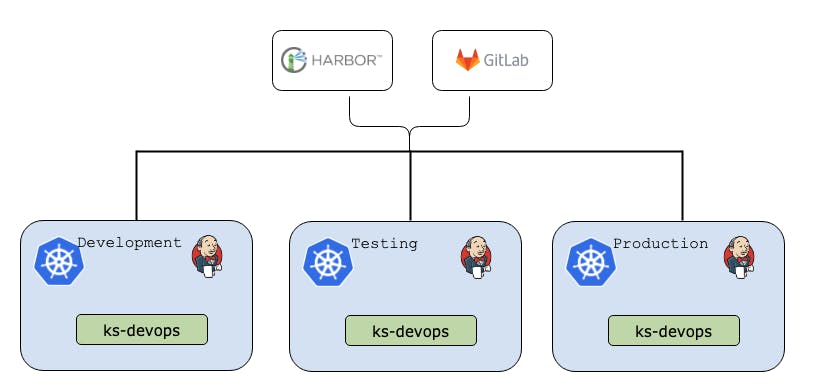
Use Cases of Kubesphere
Multi-cluster Deployment
It is generally believed that using as few clusters as possible can reduce costs with less pressure for O&M. That said, both individuals and organizations tend to deploy multiple clusters for various reasons. The main reasons for employing this method fall into the following four categories:
High Availability
Users can deploy workloads on multiple clusters by using a global VIP or DNS to send requests to corresponding backend clusters. When a cluster malfunctions or fails to handle requests, the VIP or DNS records can be transferred to a health cluster.
Low Latency
When clusters are deployed in various regions, user requests can be forwarded to the nearest cluster, greatly reducing network latency. Isolation
Failure Isolation.
Generally, it is much easier for multiple small clusters to isolate failures than a large cluster. In case of outages, network failures, insufficient resources or other possible resulting issues, the failure can be isolated within a certain cluster without spreading to others.
Business Isolation.
Although Kubernetes provides namespaces as a solution to app isolation, this method only represents the isolation in logic. This is because different namespaces are connected through the network, which means the issue of resource preemption still exists.
Avoid Vendor Lock-in
When users deploy applications, they can decide to which Kubernetes cluster they want app replicas to be scheduled in the pool. The whole process is managed and maintained through KubeSphere. This is how KubeSphere helps users achieve multi-site high availability (across zones and clusters).
Full-stack Observability with Streamlined O&M
Observability represents an important part in the work of Ops teams. In this regard, enterprises see increasing pressure on their Ops teams as they deploy their business on Kubernetes directly or on the platform of other cloud providers. This poses considerable challenges to Ops teams since they need to cope with extensive data.
Multi-dimensional Cluster Monitoring
Ops teams are in desperate need of a unified view across different clouds for cluster monitoring covering metrics across the board.
Log Query
A comprehensive monitoring feature is meaningless without a flexible log query system. This is because users need to be able to track all the information related to their resources, such as alerting messages, node scheduling status, app deployment success, or network policy modification.
Customization
KubeSphere features a unified platform for the management of clusters deployed across cloud providers. Apps can be deployed automatically, streamlining the process of operation and maintenance.
At the same time, KubeSphere boasts powerful observability features (alerting, events, auditing, logging and notifications) with a comprehensive customized monitoring system for a wide range of resources. Users themselves can decide what resources they want to monitor in what kind of forms.
Implement DevOps Practices
With KubeSphere, enterprises can make full use of DevOps by:
- Testing service robustness through fault injection without code hacking.
- Decoupling Kubernetes services with credential management and access control.
- Visualizing end-to-end monitoring process.
Installing Kubesphere on Kubernetes
Perform the following steps to install KubeSphere:
- Run the following commands to start installation:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubesphere/ks-installer/releases/download/v3.2.1/kubesphere-installer.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubesphere/ks-installer/releases/download/v3.2.1/cluster-configuration.yaml
- After KubeSphere is successfully installed, you can run the following command to view the installation logs:
kubectl logs -n kubesphere-system $(kubectl get pod -n kubesphere-system -l app=ks-install -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -f
- Use kubectl get pod --all-namespaces to see whether all Pods are running normally in relevant namespaces of KubeSphere. If they are, check the port (30880 by default) of the console by running the following command:
kubectl get svc/ks-console -n kubesphere-system
Make sure port 30880 is opened in your security group and access the web console through the NodePort (IP:30880) with the default account and password (admin/P@88w0rd).
After logging in to the console, you can check the status of different components in System Components. You may need to wait for some components to be up and running if you want to use related services.
Conclusion
You have learned about KubeSphere, getting started and its features and architectures. KubeSphere is a full-stack solution for automated IT operations with a streamlined DevOpsn Workflow.
Resources
Kubesphere Website - kubesphere.io
